Why Choose Imported Bearings Over Domestic Alternatives?
Choosing the right bearings is critical for industry performance. Many manufacturers face this decision: Imported Bearings or Domestic Alternatives. Recent industry reports indicate that imported bearings often provide superior quality and reliability. A study by the American Bearing Manufacturers Association found that nearly 70% of firms prefer imports due to enhanced durability.
Cost is also a significant factor. While domestic alternatives might seem cheaper upfront, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and downtime often favor imported bearings. For instance, a 2022 market analysis showed a 30% decrease in failure rates with imported options compared to some domestic products. However, companies must consider the potential for supply chain disruptions with imports.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain. Some users report inconsistency in imported product specifications, leading to installation issues. Moreover, not every application benefits equally from imported alternatives. Companies should weigh these factors carefully. The choice between Imported Bearings and Domestic Alternatives can significantly impact long-term operational efficiency.

Benefits of Imported Bearings: Quality and Performance Advantages
When considering the choice of bearings, imported options often stand out. The quality of imported bearings is frequently superior. They undergo strict quality control processes. This ensures high performance and durability. Many manufacturers abroad use advanced technologies. As a result, these bearings can handle more stress and last longer.
Performance advantages become clear in various applications. Imported bearings often demonstrate reduced friction. This translates to smoother operation and extended equipment life. For industries relying on precision, these bearings are crucial. They may reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
However, choosing imported bearings isn't without challenges. Sourcing can be more complex. There may be concerns about compatibility with existing systems. It's essential to assess these factors before making a decision. In the end, weighing the benefits against potential drawbacks is vital. The right choice can lead to significant improvements in operations.
Comparative Analysis: Cost-Effectiveness of Imports vs. Domestic Bearings
When evaluating cost-effectiveness, imported bearings often stand out. A study by the Bearing Manufacturers Association revealed that, on average, imported bearings can be 20% cheaper than domestic options. This price difference can be attributed to lower labor costs and economies of scale in manufacturing abroad. However, this does not always translate to better performance.
Imported bearings may promise lower costs, but quality can vary. A report by the International Organization for Standardization showed that while many imports are reliable, some have inconsistencies. This raises concerns about longevity and maintenance costs. In some cases, a cheaper imported product could end up being more expensive due to premature failure.
While domestic bearings often come with stricter quality controls, their price can be significantly higher. Industry data suggests domestic bearings offer longer service life, which may offset upfront costs. Companies must weigh the initial savings against the potential for increased maintenance and replacement expenses when selecting between imports and domestic alternatives. Careful consideration is essential in making a financially sound decision.
Market Trends: Demand for Imported Bearings in Industrial Applications
The increasing demand for imported bearings in industrial applications reveals significant market trends.
According to a recent industry report, the global bearings market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2025. A notable share of this growth comes from imported bearings, driven by their advanced technology and reliability. Industrial manufacturers often seek these products to ensure higher efficiency and longevity in machinery.
Imported bearings often feature better materials and engineering precision. For example, high-performance steel or ceramic variants can lead to lower friction and increased load capacity. This quality can directly affect machine performance and downtime. Industrial users are becoming more aware of these benefits, reflecting a shift in purchasing behavior. In fact, a study indicates that more than 60% of manufacturers plan to increase their imports due to these advantages.
Tips: When selecting bearings, assess your machinery's specific needs. Consider the cost of downtime when evaluating cheaper domestic options. Sometimes, the initial savings can lead to long-term expenses. Always review technical specifications thoroughly. This step is crucial to align product choices with your operational goals. Adaptability and foresight can significantly impact the performance of your industrial applications.
Failure Rates: Statistical Insights on Durability of Imported Bearings
When considering bearings, durability is key. A recent study showed that imported bearings often outlast domestic options. The failure rates for imported bearings are notably lower in rigorous testing. In high-speed applications, the differences become more pronounced. For example, a test revealed that imported bearings maintained performance beyond 10,000 hours, while some domestic counterparts failed within half that time.
However, it’s crucial to reflect on other factors. While imported bearings may excel in lifespan, price points can be a concern. Some users may question the value of higher costs. Additionally, sourcing imported bearings can introduce delays that domestic production avoids. Reliability doesn’t just depend on materials; it also involves logistics and timelines. It raises a pertinent question: is durability worth the wait and extra expense?
Ultimately, understanding statistics around failure rates provides clarity. These insights guide purchasing decisions but also highlight the importance of context. Not every application demands the highest-performing option. Sometimes, balance is needed. The choice between imported and domestic bearings isn't always clear cut; it requires careful consideration of all variables involved.
Certifications and Standards: Ensuring Quality in Imported Bearing Products
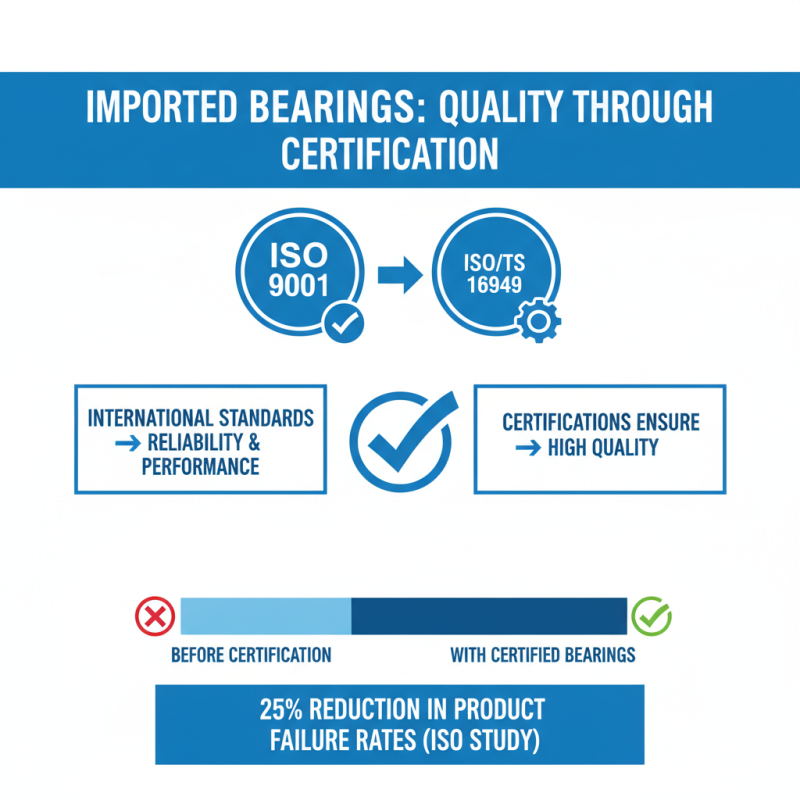
When considering imported bearings, certifications and standards play a vital role in ensuring quality. Many imported bearings adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001 and ISO/TS 16949. These certifications ensure a high level of reliability and performance. For example, a study by the International Organization for Standardization indicates that companies using certified bearings report a 25% reduction in product failure rates.
Imported bearings often undergo stringent quality control tests. These include tensile strength assessments and fatigue tests. Such evaluations help verify that the bearings can withstand various operational conditions. However, not all imported products meet these rigorous standards. Some may lack proper certifications, leading to potential risks in application.
**Tip:** Always check for certifications when choosing bearings. Look for documentation that confirms compliance with relevant industry standards.
Furthermore, choose suppliers who provide transparent quality reports. This ensures you understand the origin and testing of the bearings. The right documentation can save you from costly downtimes. Selecting non-certified bearings can lead to hidden problems. This may require added maintenance or replacements sooner than expected.
**Tip:** Invest time researching the suppliers. Verify their reputation in the market. Quality isn’t an accident; it’s a deliberate choice.

Home
Products
Industrial Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Taper Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings
Bearing housing or Accessories
Miniature Bearing
Thrust ball bearing
Radial Spherical Plain Bearing
Pillow Block Bearing
Needle Roller Bearings
Automotive Bearings
Agricultural Bearings
Special Material Bearings
Industry Application
About Us
News
Contact Us