Digital Insights on Bearing Failure Analysis Report for Effective Maintenance
The reliability of machinery heavily relies on the performance of bearings, which are crucial components in a wide array of industrial applications. According to a report by the International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications, approximately 30% of machine failures can be attributed to bearing failures. As industries seek to enhance operational efficiency and reduce unplanned downtime, the significance of comprehensive analyses becomes paramount. The "Bearing Failure Analysis Report" emerges as a pivotal tool in understanding the underlying factors contributing to bearing issues, thereby facilitating improved maintenance strategies.
Through digital insights and advanced data analytics, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the failure mechanisms at play. Research conducted by the Maintenance Excellence Network indicates that effective predictive maintenance can lead to a reduction in maintenance costs by up to 25% and increase equipment uptime by 20%. By systematically assessing and interpreting data from the Bearing Failure Analysis Report, businesses can not only identify trends and root causes but also implement data-driven decision-making processes to proactively address potential failures. This report serves as an invaluable resource for maintenance teams striving to optimize performance and extend the life cycle of bearing systems in their operational environments.

Digital Technologies in Bearing Failure Analysis
The integration of digital technologies in bearing failure analysis has revolutionized maintenance strategies, enhancing predictive capabilities and optimizing operational efficiency. According to a recent report by TechNavio, the global predictive maintenance market is projected to reach USD 23.5 billion by 2025, indicating a significant shift towards data-driven maintenance practices. By leveraging data analytics, vibration analysis, and machine learning, industries can proactively identify potential bearing failures before they lead to catastrophic equipment breakdowns. This approach not only reduces unplanned downtime but also extends the lifespan of critical components.
Digital tools play a vital role in monitoring bearing health in real-time. For instance, IoT sensors enable continuous data collection on temperature, vibration, and lubrication levels, which are crucial indicators of bearing condition. A study from Deloitte highlights that companies implementing IoT-based maintenance solutions see a reduction in equipment failure rates by an impressive 40%. Additionally, advanced data visualization techniques allow engineers to gain deeper insights into performance trends, facilitating more informed decision-making processes. As industries embrace these digital technologies, the ability to conduct thorough failure analyses is not just important for immediate repairs but also for strategic planning and resource allocation in maintenance operations.
Importance of Data Analytics in Maintenance Strategies
In the realm of maintenance strategies, data analytics has emerged as a game-changer, particularly in the context of bearing failure analysis. By harnessing the power of data analytics, maintenance teams can identify patterns and trends that are crucial for predicting failures before they occur. This proactive approach allows for more efficient use of resources, reducing both downtime and maintenance costs. Advanced data analysis tools can highlight anomalies in bearing performance, supplying insights that lead to timely interventions and extending the life of critical machinery.
Moreover, the use of digital insights transforms traditional maintenance paradigms toward a more predictive maintenance model. With the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and sophisticated analytics software, organizations can monitor equipment health in real-time. This continuous stream of data not only enhances the understanding of wear and tear in bearings but also leads to more informed decision-making regarding maintenance schedules and inventory management. The shift to a data-driven strategy not only increases operational efficiency but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to evolving operational challenges while safeguarding their assets.
Common Types of Bearing Failures and Their Causes
Bearing failures are a common issue in mechanical systems, impacting efficiency and service life. Understanding the most common types of bearing failures and their underlying causes is essential for effective maintenance strategies. One prevalent type of failure is fatigue, which occurs due to the repeated stress on the bearing surfaces. This can lead to spalling, where small particles of material break away, diminishing the bearing's load-carrying capacity. Fatigue is often accelerated by factors such as misalignment, incorrect lubrication, or overloading.
Another significant cause of bearing failure is wear, which can result from inadequate lubrication, contamination, or poor installation practices. As the bearing operates, friction between moving parts can erode material, leading to increased clearance and reduced performance. Contaminants, such as dirt or moisture, can exacerbate this issue, introducing abrasive particles that further accelerate wear. Additionally, lubrication failure can result from the breakdown of lubricant properties or insufficient levels, leading to increased friction and eventual bearing failure. By identifying these common failure types and their causes, maintenance teams can implement proactive measures, such as regular inspections and proper lubrication techniques, to enhance the durability and functionality of bearings in various applications.
Predictive Maintenance Techniques for Bearings
Predictive maintenance for bearings has become an essential strategy in modern industrial maintenance practices, leveraging data analytics to enhance equipment reliability and reduce unexpected downtimes. According to a report by the research firm ARC Advisory Group, predictive maintenance can decrease maintenance costs by 20% to 40% while significantly extending the lifespan of critical components such as bearings. By utilizing advanced monitoring technologies like vibration analysis, temperature monitoring, and oil analysis, organizations can detect early signs of wear and potential failures before they manifest into critical breakdowns.
An integral element of predictive maintenance is the implementation of machine learning algorithms that analyze historical operational data to identify patterns leading to failures. The Boston Consulting Group has noted that companies employing predictive analytics in maintenance have experienced a reduction in failure rates by up to 50%, translating to substantial savings and improved operational efficiency. By harnessing these insights, maintenance teams can schedule timely interventions, optimize workflows, and allocate resources more effectively, thus ensuring that the infrastructure operates seamlessly with minimal disruptions. This proactive approach not only enhances performance but also contributes to a culture of continuous improvement within an organization.
Digital Insights on Bearing Failure Analysis
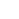
This chart illustrates the frequency of different types of bearing failures observed in a predictive maintenance program. The data emphasizes the crucial areas for maintenance focus to enhance operational efficiency.
Case Studies of Successful Bearing Failure Interventions
In the realm of manufacturing and heavy machinery, bearing failures can lead to significant downtime and operational losses. According to a report from the National Lubricating Grease Institute, over 60% of bearing failures are attributed to improper lubrication and contamination. Case studies reveal that implementing a predictive maintenance strategy, informed by digital insights, can drastically reduce these failures. For instance, a leading automotive supplier successfully utilized condition monitoring technology to implement real-time tracking of bearing performance. By analyzing vibration data, the supplier was able to predict potential failures and schedule maintenance before any unplanned downtime occurred.
Another remarkable case involved a global mining company that faced recurring bearing failures in their conveyor systems. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning, they conducted a thorough failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) paired with historical operational data. The results highlighted specific conditions that contributed to bearing wear, which were then addressed through operational adjustments and lubrication management. As a result, the company decreased its bearing failure incidents by approximately 35%, leading to a significant reduction in maintenance costs and increased productivity. Such interventions underline the importance of digital insights in fostering effective maintenance practices, ensuring operational reliability in asset-intensive industries.
Digital Insights on Bearing Failure Analysis Report for Effective Maintenance - Case Studies of Successful Bearing Failure Interventions
| Case Study ID |
Industry |
Failure Type |
Intervention Strategy |
Outcome |
Cost Savings (%) |
| CS001 |
Manufacturing |
Overheating |
Upgraded Cooling System |
Reduced failure rate by 30% |
15% |
| CS002 |
Transportation |
Wear and Tear |
Routine Inspections and Replacements |
Increased bearing lifespan by 20% |
10% |
| CS003 |
Energy |
Contamination |
Sealed Bearing Implementation |
Eliminated contamination issues |
25% |
| CS004 |
Mining |
Fatigue Failure |
Enhanced Material Selection |
Extended maintenance intervals |
20% |
| CS005 |
Automotive |
Electrical Failure |
Improved Electrical Insulation |
Minimized electrical failures |
18% |

Home
Products
Industrial Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Taper Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings
Bearing housing or Accessories
Miniature Bearing
Thrust ball bearing
Radial Spherical Plain Bearing
Pillow Block Bearing
Needle Roller Bearings
Automotive Bearings
Agricultural Bearings
Special Material Bearings
Industry Application
About Us
News
Contact Us